A cross linkable data broker chain with smart data contracts
XDV Protocol
or Any Document Verifiable Protocol
Abstract
XDV Protocol objective is to make any document or metadata, linked data or linked tokens, verifiable within decentralized stores like Filecoin, decentralized content network like IPFS or hybrid decentralized content network with blockchain features like Arweave or Swarm Bee. Verifiable Documents can be a verified credential as proposed by the Verifiable Credentials model, an ERC-721 standard NFT (Non Fungible Token), a PKCS#11 or PKCS#12 signed document verifiable with government mandated smart cards or as simple as any binary data signed with a DID that can be authenticated and verified with a proof (eg proof of residence from a KYC Know Your Customer).
Previous Work
XDV initially focused on wallets and having those wallets be able to sign documents with government mandated smart cards.
A second feature came later where the document was anchored to a blockchain. XDV worked with Swarm V1, which eventually shutdown and went to focus on Swarm Bee. XDV project team moved to IPFS while the new Swarm Bee blockchain was under construction. Note, we plan to get back to Swarm Bee in the coming weeks for our current https://firmas.xdv.digital app.
One feature requested was to preserve privacy, encryption or zero knowledge technologies were required. After looking for previous work, we stumble upon Ceramic blog and found How to Store Signed and Encrypted Data On IPFS.
We took that paper as base layer for our implementation with a few twists:
- No server changes: Customized IPFS implementation are difficult to maintain.
- Keep it simple: dag-cbor instead of dag-jose.
- Delegate missing features to other stacks: Subscriptions, events and encryption can be done by other complementary APIs.
Another previous work that we manage to create innovation around it is did-jwt. We forked did-jwt and created did-jwt-rsa, which is a DID JWT that signs and verifies RSA Signatures. By accomplishing that, we practically gain DID compatibility with PKCS#11/PKCS#12, which in most governments around the world are required for legal document signing.
And then we asked ourselves, what if you could do a RSA Signature enabled blockchain? We found out that there is actually one project, NDID blockchain from Thailand, which is developed with Tendermint.
Enter XDV: The need for custom tailor made blockchain
Initially, Substrate was the top pick, but after much research about market conditions (right now is pretty difficult to find Rust engineers) and current team knowledge, we went with Cosmos SDK and Starport.
Most of the APIs required to build XDV Protocol are in Go. A first protocol draft must contain the basic primitives, and further protocol versions must be able to build on previous work.
Considering that signature is just one of the many use cases, and that disparate data sources and structures will be more common in the future, XDV Protocol lingua franca is based in IPLD Schemas from Protocol Labs.
Thus, the current XDV Protocol Specification:
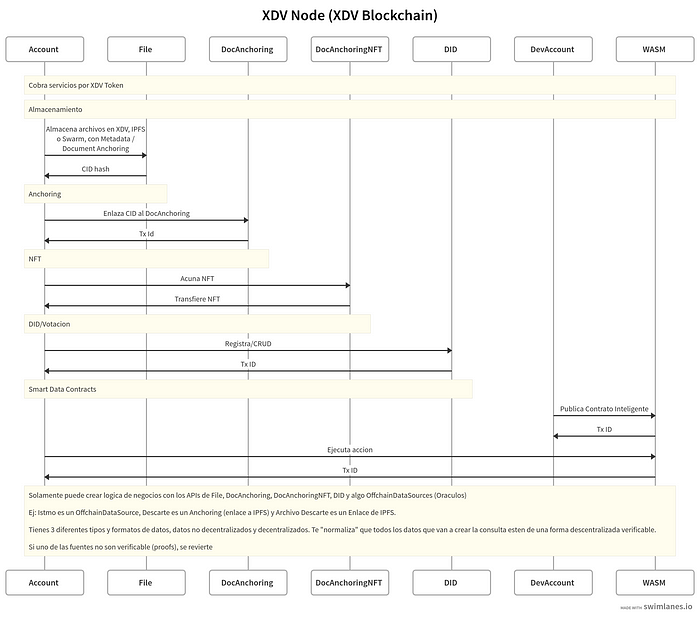
Primitives
- Files: Decentralized content storage content
- Documents: Document anchoring
- NFT: NFT (Tokenized Metadata or Non Fungible Token)
- OffchainDataSources: An ODBC inspired oracle based connection
Smart Data Contracts
- Smart Data Contracts uses the underlying primitives as API to build next generation ETL / Map Reduce like functions, where every data node is linkable and verifiable.
RBAC And ACL (Role Based Access and Access Control Lists)
Allows to configure access controls on data nodes and sources.
Use Cases
Insurance Claims
An `insurance policy` is created with automated legal tech and is connected or integrated with the issuer of the policy.
Insurance brokers or directly via website, sells policies to end users. They can get the policy by mail or in digital form. The issuer has decided to use public blockchains to be more transparent, and the broker has decide to use the issuer company REST API to start moving the previous centralized.
To listen and execute next flow, the claim will require additionally integration linked to brokers, issuer (insurance), policy holders agents (VC agent) and other offchain data sources.
- `Claim` is filed thru decentralized automated legal tech (`broker`) and sent to insurance company.
- `Policy` is verified by back office and updated in centralized solution. `Broker` has one of 5 trusted XDV Node with offchain worker connected to centralized API.
- After XDV Nodes come to a consensus, an event triggers a `smart data contract` and orchestrate trusted data which then is computed and notified to subscribers
EDI Orders and Invoicing
A XDV Node network of 7 peers is setup to integrate EDI orders with offchain workers. The grocery consortium each one has different types of data structures, they are looking for:
- Verify EDI orders signed with RSA
- Convert them to electronic invoice and cloned to XDV Node XDV Storage and configure with RBAC/ACL
- Push invoice to government tax office with government mandated signature using `smart data contracts`
COVID-19 verifiable data warehousing
In this use case, you have a pharmaceutical company, government and patients. To keep the diverse data verifiable and able to be query and used for other, non transactional uses, and because cost savings is very important in these implementations, they decide to use XDV Node and implement XDV protocol as following:
- Pharma company has their vaccine data in Ethereum private blockchain, because is private, decentralized chain, it can be thought as a sidechain. These transactions can be duplicated in XDV Node, and keep the data with selective disclosure or encrypted using XDV or IPFS Storage.
- Government keeps its data in CSV Tabular format. They would like to keep these as usual, with XDV Node, because it uses IPLD Schemas, the government selects the codec format for JSON Table. Any request from the data will be render and store as JSON Table. For this to work, they’ll need to add 3 or 5 oracle which will sync with XDV Node. Because each oracle will use BLS to sign for proof, it should be more secure than other providers.
- Patients get mobile and desktop DApps to keep track of news and events.
Pharma and Government, besides the transactional integration which keeps accountability of vaccine success, can also create `smart data contracts`. A `smart data contract` aggregates, orchestrate and maps linked, verifiable data from the chain transactions and connected.
— Industrias de Firmas Electronicas SA, Industrias DAO and Fernando Romero Copyright June 2021
